In the critical race against time that is stroke treatment, every second truly counts. For millions living in remote or underserved areas, geographical distance often translates into devastating delays, where precious brain cells die by the minute. Enter the transformative power of remote robotics, poised to bridge these gaps and redefine access to life-saving neurovascular procedures.
The Urgency of Stroke Care: Time is Brain
A common and severe type of stroke, caused by large blood clots, is typically treated with a procedure called endovascular thrombectomy (EVT). This intricate intervention requires an experienced surgeon to navigate catheters through blood vessels to the blockage, often guided by X-ray imaging. The challenge? The expertise required for EVT is often concentrated in major metropolitan hospitals, leaving patients in rural areas hours away from crucial care.
As neurologists often emphasize, “time is brain.” During a stroke, an astonishing 2 million neurons can perish every minute blood flow is interrupted. Delays of even a few hours can equate to years of typical age-related brain cell loss, leading to severe disability or even death. This stark reality highlights the urgent need for innovative solutions that can bring specialized care closer to every patient, regardless of their location.
Robotics to the Rescue: Pioneering Remote EVT
The exciting solution lies in advanced telerobotics. Imagine a specialized robotic system situated in a smaller community hospital, controlled by an expert neurosurgeon located hundreds or even thousands of miles away. This is no longer a futuristic vision but a rapidly unfolding reality.
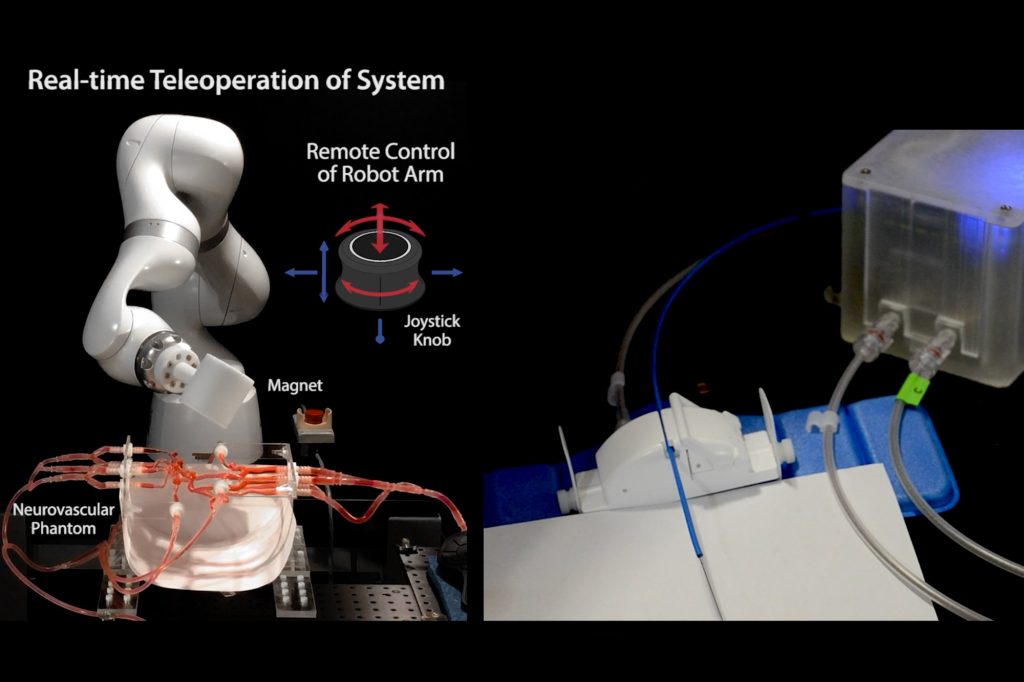
Two leading innovators, Remedy Robotics and Sentante, have recently showcased remarkable progress in remote EVT capabilities. Remedy Robotics successfully facilitated a series of brain angiograms between Toronto hospitals using its N1 system. Simultaneously, Sentante demonstrated a simulated EVT procedure between a surgeon in Florida and a cadaver in Scotland, proving the feasibility of transatlantic robotic control.
Two Distinct Approaches to Remote Precision
While both companies are pushing the boundaries of remote neurointervention, they employ distinct technological philosophies:
- Remedy Robotics (N1 System): This system heavily leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Its device is designed to autonomously assist in manipulating guide wires and provides an intelligent informational overlay on X-ray images for remote physicians. Surgeons can control the robot via a laptop and a sophisticated software interface, with the long-term vision of a single surgeon remotely managing multiple robots across various hospitals. Remedy has also prioritized robust connection monitoring to prevent harmful movements during connectivity issues.
- Sentante: In contrast, Sentante focuses on a more tactile and intuitive experience. Their control console is meticulously designed to mimic the look and feel of traditional catheters and guide wires, incorporating force feedback that replicates the resistance a surgeon would feel during an in-person procedure. This naturalistic haptic feedback was crucial in their transatlantic demonstration, with reported latency around 120 milliseconds. While not yet implemented, Sentante plans to integrate AI by collecting vast amounts of training data from images and force measurements.
Overcoming Challenges and Paving the Way for Clinical Use
The journey to widespread clinical adoption involves addressing critical factors like maintaining strong, low-latency connections over vast distances and defining the role of bedside assistance. Both companies are committed to ensuring connection reliability and streamlining the interaction required from on-site healthcare providers. Remedy, for instance, has engineered its robot to handle as much of the procedure as possible, minimizing the burden on local staff.
The regulatory path often involves initial approval for local, on-premise endovascular procedures, with remote applications following. Remedy has clinical trials planned for 2026 for local neurointerventions and has partnered with the Australian Stroke Alliance for future remote trials. Sentante’s system is eyeing market entry in the EU next year for peripheral vascular interventions and has already secured a breakthrough device designation from the U.S. FDA for remote stroke treatment. Other players like Corindus (now with Siemens) and Xcath are also contributing to this burgeoning field.
A Future of Accessible, Advanced Healthcare
The advent of remote robotics in stroke treatment promises a future where geographical barriers no longer dictate access to life-saving care. By bringing expert surgical capabilities to patients in any location, these innovations have the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes, reduce disability, and preserve countless years of quality life. It’s an exciting era for neurointerventionalists and, more importantly, for patients worldwide.
Connect with the CTO ROBOTICS Media Community
Follow us and join our community channels for the latest insights in AI, Robotics, Smart Manufacturing and Smart Tech.
CTO Robotics
CTO Robotics is a global media and consulting company dedicated to robotics, automation, artificial intelligence, and emerging technologies. We create high-impact content that reaches engineers, decision-makers, and innovators worldwide. Through articles, videos, social media campaigns, and community-driven storytelling, we help companies showcase their technologies, strengthen their brand, and connect with the right audience. Much like Interesting Engineering or Wevolver, our mission is to bridge the gap between technology providers and industry professionals — turning innovation into visibility, and visibility into growth. 👉 Whether you are launching a new product, building your brand, or looking for global recognition, CTO Robotics is your media partner for exposure, credibility, and business opportunities.
All stories by: CTO Robotics












0 Comments